Introduction
本系列机器学习来自于台湾大学-林轩田老师的课堂的学习总结。

Foundation Oriented ML Course
从基础开始学习,机器学习基石。
When can machines learn? (illustrative + technical)
课程介绍
什么是机器学习
学习是获取技巧的过程,学习是从观察开始的。
人类学习: 观察 -> 学习 -> 技巧。 机器学习: data -> ML -> skill。
技巧:某种表现的增进。
机器学习:improving some performance measure with experience computed from data.
一些应用:辨识图中是否有一颗树。树如何定义呢?(用什么样的规则呢?)让机器自己去分析资料,自己去学会如何辨识一颗树。
机器学习使用的场合:
- when human cannot program the system manually : navigating on Mars
- when human cannot ‘define the solution’ easily : speech/visual recognition
- when needing rapid decisions that humans cannot do : high-frequency trading
- when needing to be user-oriented in a massive scale : consumer-targeted marketing
机器学习的三个关键:
- exists
some 'underlying pattern' to be learned: so ‘performance measure’ can be improved. - but no programmable (easy) definition : so ‘ML’ is needed.
- somehow there is data about the pattern : so ML has some ‘inputs’ to learn from.
个人理解:机器学习的三个关键就是说,机器学习需要从一堆数据中学习一些不容易定义的规则来提高他们的表现。
机器学习的应用
- Food
- data: Twitter data
- skill: tell food poisoning likeliness of restaurant properly
- Clothing
- Housing
- Transportation
- Recommender System
- …
机器学习的组成
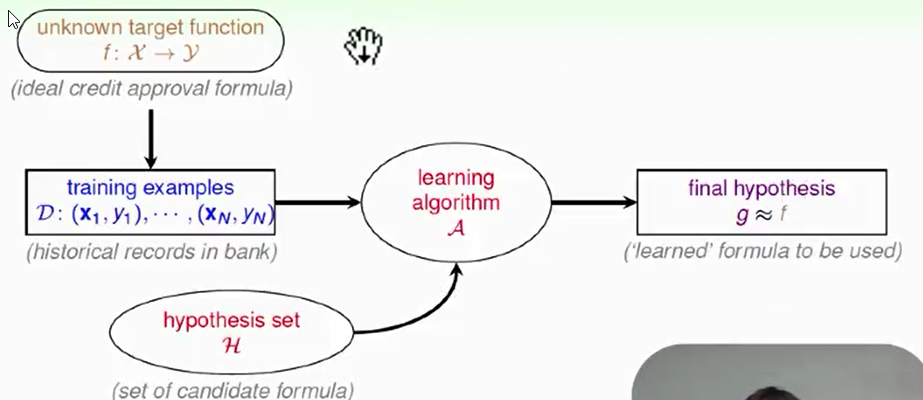
A takes D and H to get g.a
Basic Notations:
- input: x
- output: y
- unknown pattern to be learned <=> target function: f : x -> y
- data <=> training examples: D = {}
- hypothesis <=> skill with hopefully good performance: g : x -> y
总结为:
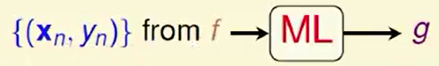
以是否授权信用卡为例:期待的效果是效能的增进,即 g 跟 f 越像越好,越像 g 就越棒。机器学习最后能够得到一个 g 和 f 很像。
- f 未知
- 但是 g 跟 f 越像越好
hypothesis set H: 包含 good 或者 bad hypotheses。
其中 g 属于 H(hypothesis set), learning algorithm A 要做的事情就是从看到的数据 data 中,去集合 H 中,选一个最好的出来。
因此,机器学习可以看做是有两个输入:一个是 data,另一个是允许它选哪些 hypothesis?
以后讲到的模型,就指的是演算法 learning algorithm A 以及 hypothesis set 使用的大 H 部分,这两个集合合起来叫做一个模型。
整个机器学习的流程如下图:机器学习就是从数据 data 出发,机器学习演算法 learning algorithm A 要算出一个 hypothesis g,希望这个 g 要和真正的 f 很接近。
机器学习和其他领域
- Machine Learning:use data to compute hypothesis g that approximates target f.
- Data Mining: use (huge) data to find property that is interesting。Difficult to distinguish ML and DM in reality.
- Artificial Intelligence: compute something that shows intelligent behavior. Ml is one possible route to realize AI.
- Statistics: use data to make inference about an unknown process. statistics can be used to achieve ML.